As society and more and more governments call for zero-emissions initiatives - see the Hamburg city council, which will no longer allow new combustion engines for taxis from 2025 - the need for accurate insights into these initiatives is also increasing.
To understand the impact of their emission reduction initiatives, companies are often confronted with the question of how to measure and report these initiatives.
In our last blog post on the European Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), we explained the basics of the CSRD and helped you understand how it affects your company's sustainability management.
With this in mind, in this article we explain how to determine your company's CO2 emissions, the industry standard for doing so and what you can do to prepare for the CSRD reporting requirements.
To make it practical, let's go through in three steps why NAVIT chose SQUAKE as a partner to make sustainability core to employee mobility - from raising awareness of emissions to reporting and offsetting.
What is the CSRD?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, or CSRD, is an EU directive on corporate sustainability reporting and was adopted by the European Council on 28 November 2022 as part of the EU Green Deal. The CSRD updates and expands the scope of sustainability reporting requirements introduced by the existing Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) in 2014. This change in legislation means that all large companies will be held publicly accountable for their impact on people and the environment.
With the new CSRD guidelines, almost 50,000 companies will have to prepare for compliance, compared to about 11,000 companies under the previous NFRD framework. Most likely, your company will also be affected by the CSRD.
The CSRD has two objectives:
The following timetable for the implementation of the CSRD illustrates how enforcement will take place gradually:
When will I have to report?
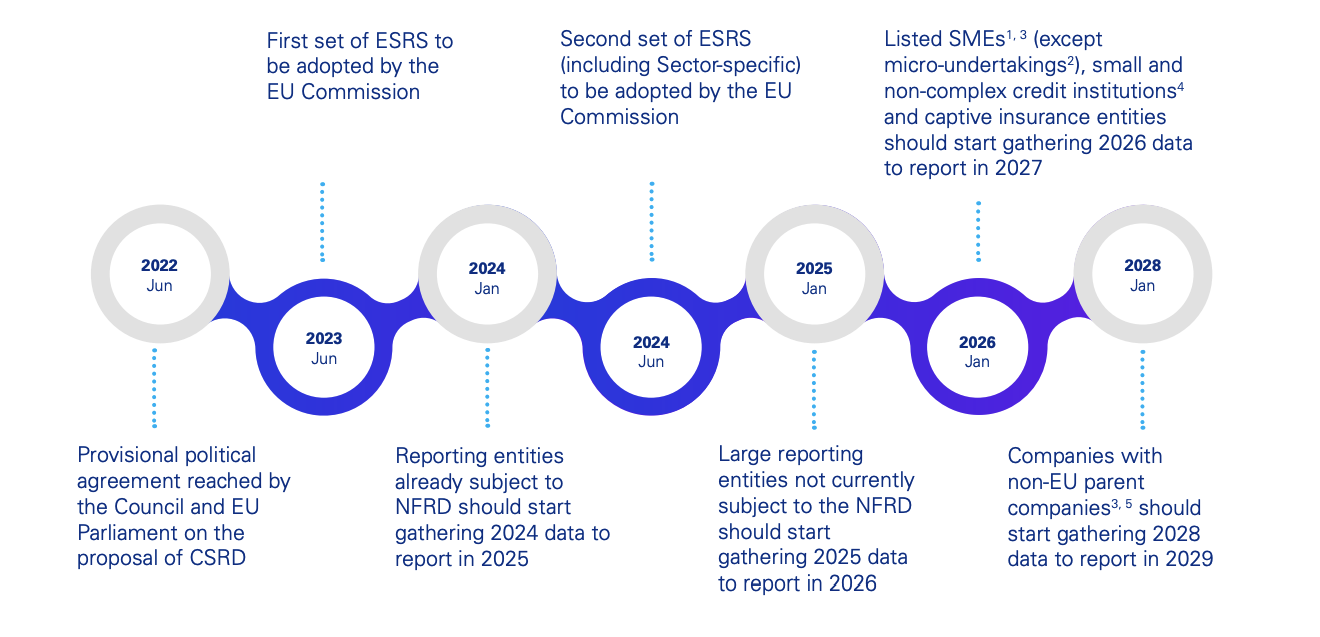
Source: "The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)" - KPMG
Regardless of the shape or size of your business, it is only a matter of time before your company needs to set up a reporting system.
These 4 steps will help you get started with reporting:
Why is employee mobility relevant to CSRD?
Employee mobility takes a central role in a company's sustainability strategy. In fact, 6% of global CO2 emissions can be attributed to employees' daily commute. Some studies even suggest that commuting accounts for up to 98% of an employee's work-related emissions. Although it is difficult for most companies to collect data on employee mobility, it is very important for them to understand it - mainly for these two reasons:

As society and more and more governments call for zero-emissions initiatives - see the Hamburg city council, which will no longer allow new combustion engines for taxis from 2025 - the need for accurate insights into these initiatives is also increasing.
To understand the impact of their emission reduction initiatives, companies are often confronted with the question of how to measure and report these initiatives.
In our last blog post on the European Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), we explained the basics of the CSRD and helped you understand how it affects your company's sustainability management.
With this in mind, in this article we explain how to determine your company's CO2 emissions, the industry standard for doing so and what you can do to prepare for the CSRD reporting requirements.
To make it practical, let's go through in three steps why NAVIT chose SQUAKE as a partner to make sustainability core to employee mobility - from raising awareness of emissions to reporting and offsetting.
What is the CSRD?
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, or CSRD, is an EU directive on corporate sustainability reporting and was adopted by the European Council on 28 November 2022 as part of the EU Green Deal. The CSRD updates and expands the scope of sustainability reporting requirements introduced by the existing Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) in 2014. This change in legislation means that all large companies will be held publicly accountable for their impact on people and the environment.
With the new CSRD guidelines, almost 50,000 companies will have to prepare for compliance, compared to about 11,000 companies under the previous NFRD framework. Most likely, your company will also be affected by the CSRD.
The CSRD has two objectives:
The following timetable for the implementation of the CSRD illustrates how enforcement will take place gradually:
When will I have to report?

Source: "The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)" - KPMG
Regardless of the shape or size of your business, it is only a matter of time before your company needs to set up a reporting system.
These 4 steps will help you get started with reporting:
Why is employee mobility relevant to CSRD?
Employee mobility takes a central role in a company's sustainability strategy. In fact, 6% of global CO2 emissions can be attributed to employees' daily commute. Some studies even suggest that commuting accounts for up to 98% of an employee's work-related emissions. Although it is difficult for most companies to collect data on employee mobility, it is very important for them to understand it - mainly for these two reasons: